Introduction to Piping Supports and Hangers
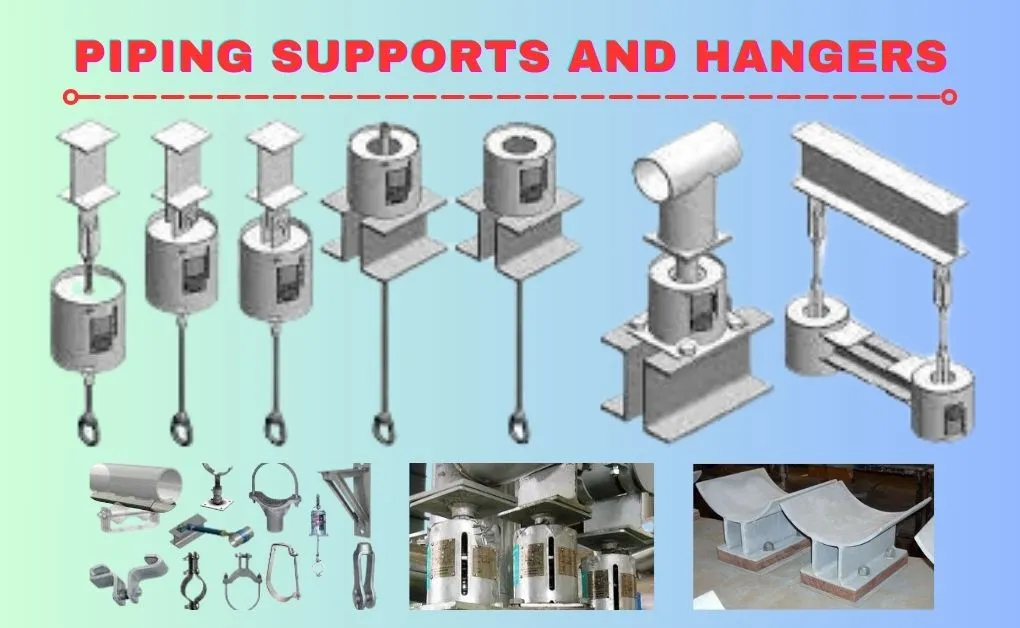
Pipe supports and hangers play a crucial role in the integrity and functionality of piping systems in various industries. From industrial plants to commercial buildings and residential homes, these components provide support, stability and protection to ensure efficient pipe operation. In this comprehensive guide, we will read about pipe supports and hangers, exploring their history, functions, types, applications, challenges, and best practices.
Understanding Piping Supports and Hangers
Piping supports and hangers are structural components designed to support, guide, and restrain piping systems. They prevent sagging, vibration, and excessive movement, thereby safeguarding the integrity of pipelines and ensuring safety in industrial and commercial environments. The evolution of piping supports and hangers has been driven by the need for reliable and cost-effective solutions to support the complex network of pipes used in various applications.
The Importance of Piping Supports and Hangers
Piping supports and hangers are essential for maintaining the stability and functionality of piping systems. Without proper support, pipes may sag, bend, or even fail under the weight of fluids, leading to leaks, downtime, and safety hazards. By distributing the load evenly and providing adequate support, piping supports and hangers help prevent damage to pipes, equipment, and surrounding structures, ultimately reducing maintenance costs and enhancing operational efficiency.
Types of Piping Supports and Hangers
There are various types of piping supports and hangers available, each designed for specific applications and operating conditions. These include:
Primary Categories of Piping Supports
1. Rigid Supports:
A) Rest Supports:
- Base Support: Provides vertical support by resting on a structural element.
- Saddle Support: Used for larger pipes, often with insulation.
B) Guide Supports:
- Line Stop: Restrains pipe movement in one direction.
- Guide: Allows axial movement but restricts lateral movement.
C) Anchor Supports:
- Fixed Anchor: Completely restricts pipe movement in all directions.
2. Flexible Supports:
A) Spring Hangers:
- Constant Spring Hanger: Maintains constant support force despite pipe movement.
- Variable Spring Hanger: Support force varies with pipe movement.
B) Spring Supports: Similar to hangers but used under pipes.
3. Dynamic Supports:
A) Snubbers:
- Hydraulic Snubber: Absorbs shock and vibration.
- Mechanical Snubber: Functions similarly but uses mechanical means.
B) Dampers: Used to reduce vibrations.
Specific Types of Piping Hangers and Supports
Pipe Clamps:
- Standard Clamp: Common for general support.
- Insulated Clamp: Used with insulated pipes to prevent heat transfer.
Hanger Rods:
- Single Rod Hanger: Used for vertical support.
- Double Rod Hanger: Provides additional stability for larger pipes.
Pipe Shoes:
- Standard Shoe: Supports and guides the pipe while allowing axial movement.
- Insulated Shoe: Prevents thermal transfer from pipe to support structure.
Pipe Rollers:
- Standard Roller: Allows axial movement, reducing friction.
- Insulated Roller: Used with insulated pipes to minimize heat transfer.
Trunnions:
- Standard Trunnion: Attached to the pipe, allowing rotation.
- Insulated Trunnion: Similar to the standard, but for insulated pipes.
Pipe Saddles:
- Concrete Saddle: Provides support and stability, often for larger pipes.
- Steel Saddle: Similar function but made of steel for different applications.
Hangers with Vibration Isolation:
- Rubber Mounts: Reduce vibration transmission.
- Spring Isolators: Provide vibration isolation with spring mechanisms.
Application Specific Supports
- Cryogenic Supports: Designed for extremely low temperatures, often involving special materials and insulation.
- High-Temperature Supports: Made from materials that can withstand high temperatures without losing strength or integrity.
- Corrosion-Resistant Supports: Used in environments where corrosion is a significant concern, often involving stainless steel or other resistant materials.
Application of Piping Supports and Hangers
Piping supports and hangers find applications in various industries, including:
- Oil and Gas: Supporting pipelines for the transportation of crude oil, natural gas, and refined products.
- Chemical Processing: Providing support for pipes carrying corrosive or hazardous chemicals in chemical plants.
- Power Generation: Supporting steam, water, and fuel pipes in power plants for electricity generation.
- HVAC Systems: Hanging ductwork and piping in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems for buildings.
- Water and Wastewater: Supporting pipes in water treatment plants, sewer systems, and distribution networks.
Challenges and Solutions
Despite their importance, piping supports and hangers face several challenges, including corrosion, vibration, thermal expansion, and seismic loads. However, advancements in materials, design, and technology have led to innovative solutions to overcome these challenges. For example, the use of corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel or fiberglass, can extend the lifespan of piping supports and hangers in corrosive environments.
Best Practices for Piping Supports and Hangers
To ensure the optimal performance and longevity of piping supports and hangers, it is essential to adhere to best practices in design, installation, inspection, and maintenance. This includes:
- Conducting thorough engineering analysis and design to determine the appropriate type and location of piping supports and hangers.
- Following manufacturer’s recommendations and industry standards for installation and assembly.
- Regularly inspecting and monitoring piping supports and hangers for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.
- Implementing preventive maintenance measures, such as lubrication, adjustment, and replacement of worn components.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, piping supports and hangers are critical components of piping systems, providing essential support, stability, and protection against various mechanical and environmental forces. By understanding the types, applications, challenges, and best practices associated with piping supports and hangers, engineers, designers, and maintenance professionals can ensure the safety, reliability, and efficiency of piping systems across different industries.
Download P_and_ID Free PDF Download P and ID example PDF Download P and ID Symbols PDF Download PDF for Mechanical supervisor and foreman roles and responsibilities Download PDF for Column or Tower maintenance procedure
Piping Question Answer Series Part – 02
Download Free PDF Part-01 Click Here
Read Also
Download Free Piping PDF for Interview Preparation
What is SMAW Welding What is gasket and their types What is a valve and its types?
