Understanding Gasket Types and Materials for Heat Exchangers
Heat Exchanger Gasket: When it comes to heat exchangers, the gaskets used play a critical role in ensuring the system operates efficiently without leaks or breakdowns. In this detailed article, we will discuss the types of gaskets used in heat exchangers, the materials involved, and their respective advantages. If you are in the oil and gas industry, chemical plants, or involved in heat exchanger maintenance, understanding these gasket types is crucial.
What Are Heat Exchanger Gaskets?
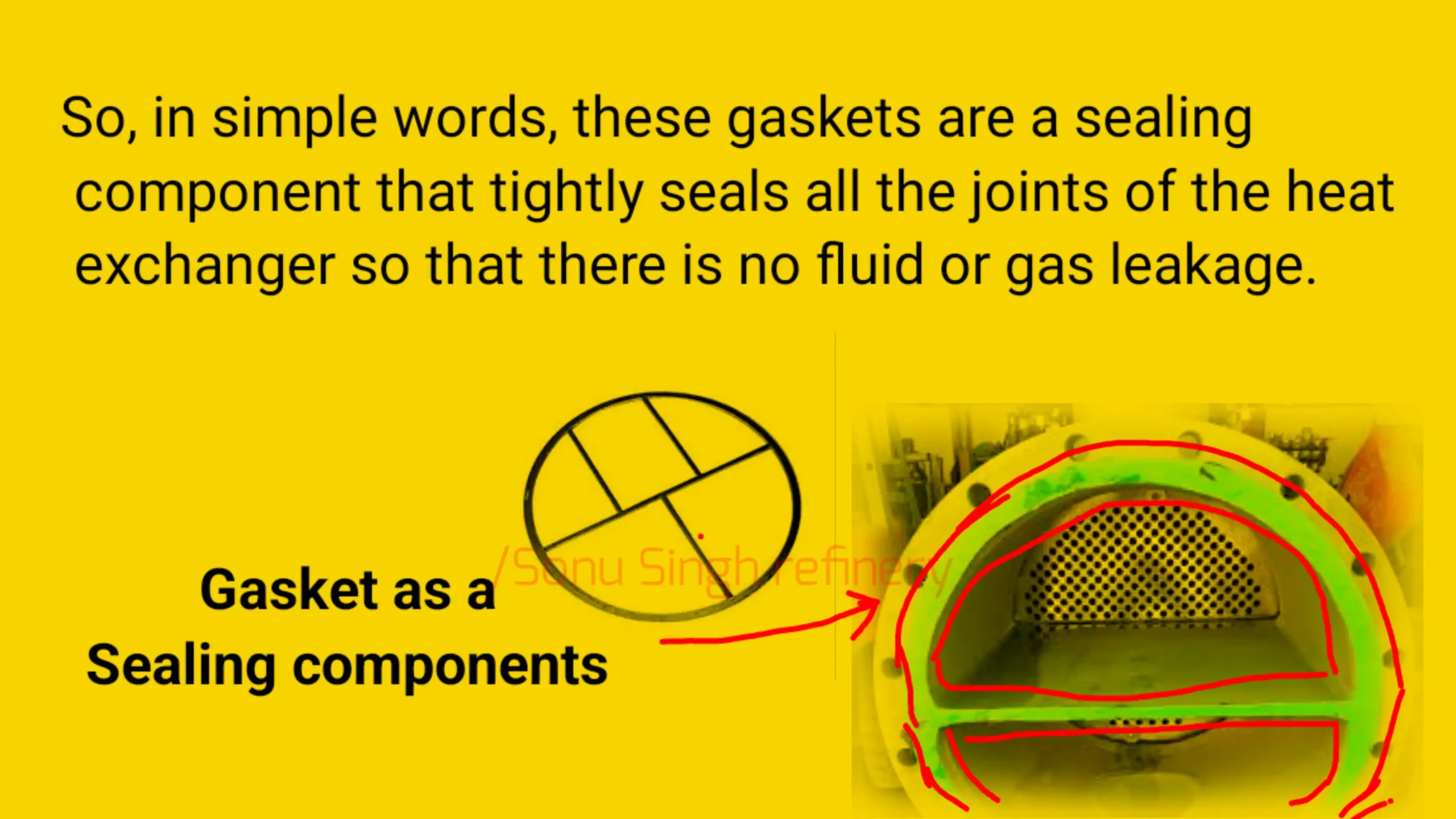
Heat exchanger gaskets are vital sealing components designed to prevent the leakage of fluids or gases within the heat exchanger system. They seal the joints where pipes and connections meet, ensuring that the heat exchange process remains efficient and leak-free. Gaskets come in a variety of shapes and sizes, tailored to fit specific heat exchanger configurations, such as the shell and tube type.
Typically, gaskets in heat exchangers have:
- Primary seals at the inner diameter, preventing leakage at critical points.
- Secondary seals at the outer diameter, acting as an extra layer of protection.
Additionally, some gaskets feature integrated bars that help seal the different passages within the heat exchanger.
Types of Gaskets for Heat Exchangers

Several gasket types are specifically designed for heat exchangers. The most common ones include:
- Double-jacketed gaskets
- Kammprofile gaskets
- Corrugated metal gaskets
- Spiral wound gaskets
Each type of gasket is ideal for different applications depending on the pressure, temperature, and fluid type.
Double-Jacketed Gaskets Explained
Double-jacketed gaskets are widely used in heat exchangers, particularly in high-pressure and high-temperature environments. These gaskets consist of a soft filler material, such as graphite, enclosed within a metallic jacket. The metal jacket provides additional strength and resistance to pressure, making them suitable for demanding applications.
Example
In the oil and gas industry, where high-temperature steam is frequently handled, double-jacketed gaskets are commonly used. These gaskets, often filled with flexible graphite, can handle temperatures up to 500°C, ensuring safety and performance even in extreme conditions.
Why Double-Jacketed Gaskets?
Double-jacketed gaskets are perfect for:
- High-temperature environments
- High-pressure conditions
- Applications requiring leak prevention
Corrugated Metal Gaskets
Corrugated metal gaskets are another essential type of gasket used in heat exchangers. These gaskets are made entirely of metal and feature a corrugated (wavy) design. The corrugations allow the gasket to compress easily, improving its sealing performance and enabling it to handle frequent temperature fluctuations.
Example
In oil refineries, corrugated stainless steel gaskets are preferred because of their ability to withstand fluctuating temperatures while maintaining a tight seal. These gaskets provide superior sealing even as the metal expands and contracts with temperature changes.
Key Benefits of Corrugated Metal Gaskets
- Ideal for applications with frequent temperature changes
- Excellent compressibility and sealing efficiency
- Commonly used in oil and gas applications
Spiral Wound Gaskets
Spiral wound gaskets are composed of alternating layers of metal windings and soft filler materials. The combination of metal and filler allows these gaskets to function effectively in high-pressure and fluctuating temperature environments. Their versatile design makes them suitable for many industrial applications.
Example
In refineries, where high pressure and elevated temperatures are common, spiral wound gaskets are often used. These gaskets feature stainless steel windings and flexible graphite fillers, ensuring durability and excellent sealing performance.
Why Choose Spiral Wound Gaskets?
Spiral wound gaskets excel in:
- Dynamic environments with changing pressure and temperature
- Refineries and chemical plants where reliability is critical
Kammprofile Gaskets
One of the most unique gasket types is the Kammprofile gasket. These gaskets feature a solid metal core with concentric grooves on the surface. The grooves are filled with a soft sealing material, such as graphite or PTFE, which helps create a tight, reliable seal. Kammprofile gaskets offer superior strength and sealing efficiency.
Example
In chemical plants, where high pressure and thermal cycling are common, Kammprofile gaskets are the go-to choice. These gaskets can withstand extreme conditions while maintaining a strong, durable seal.
Kammprofile Gaskets for Harsh Environments
Kammprofile gaskets are perfect for:
- High-pressure systems
- High-temperature applications
- Severe conditions with thermal cycling
Gaskets with Integrated and Welded Bars

Double-jacketed gaskets often feature integrated bars or welded bars. These bars help seal multiple passages within the heat exchanger. However, one common issue with these gaskets is that cracks can form at the radius area of the bars.
To address this problem, welded bar gaskets are used. These gaskets are reinforced using plasma or TIG welding, which prevents cracking and increases their long-term reliability.
Example
In natural gas plants, where stress and pressure are exceptionally high, welded bar gaskets are used to prevent cracks from forming and to maintain the structural integrity of the gasket.
Why Use Welded Bar Gaskets?
Welded bar gaskets are ideal for:
- High-stress environments
- Applications requiring long-term reliability and crack prevention
Materials Used in Heat Exchanger Gaskets
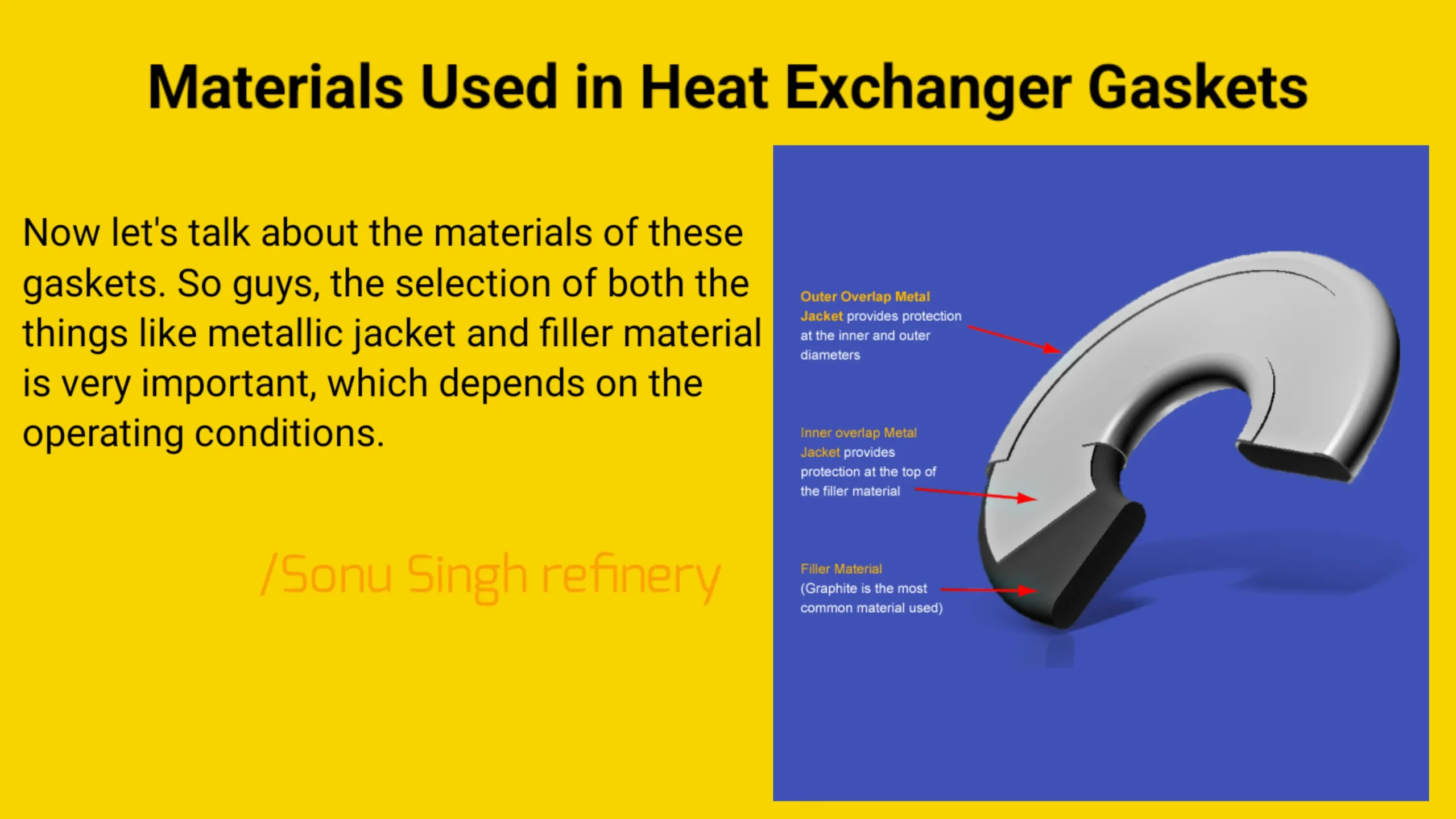
When selecting a gasket for your heat exchanger, the material used in both the metallic jacket and the filler plays a crucial role. The choice of material is typically based on the operating conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and the type of fluid being processed.
Metallic Jacket Materials

Common materials used for the metallic jacket include:
- Stainless Steel (AISI 304, 316): Ideal for corrosive environments, such as chemical processing plants.
- Monel (Alloy 400): Preferred in marine environments where saltwater resistance is required.
- Copper: Commonly used in low-temperature applications, such as water treatment.
- Titanium: Frequently used in desalination plants due to its excellent corrosion resistance.
Example
If you are working in a corrosive environment, an AISI 316 stainless steel jacketed gasket is ideal due to its resistance to harsh chemicals and corrosive agents.
Filler Materials
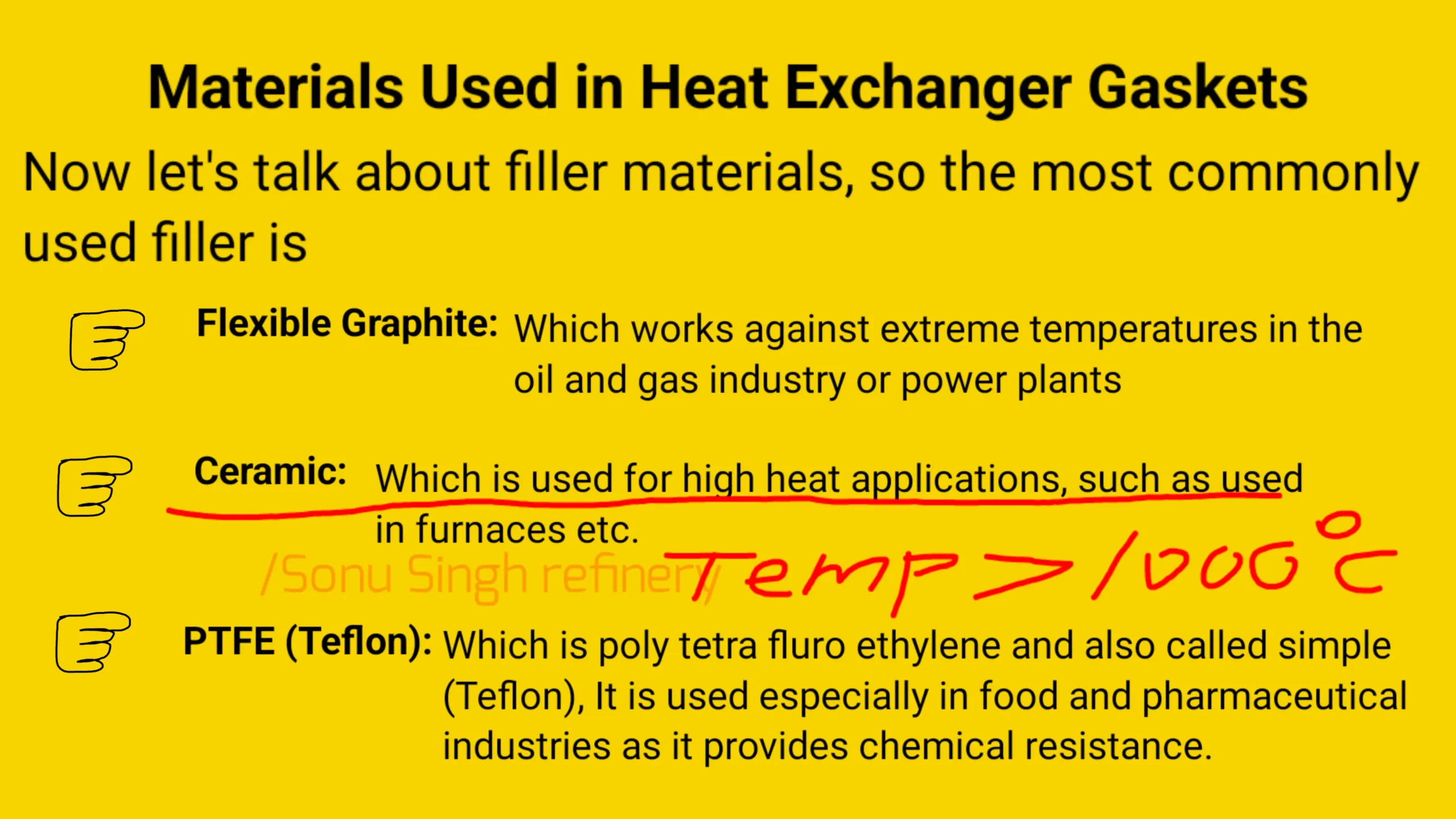
The filler material is just as important and is selected based on the specific operating environment:
- Flexible Graphite: Perfect for extreme temperatures, commonly used in power generation.
- Ceramic: Suitable for high-heat applications, such as furnaces and kilns.
- PTFE (Teflon): Commonly used in the food and pharmaceutical industries for its excellent chemical resistance.
Example
For applications where temperatures exceed 1000°C, ceramic-filled gaskets are the best option, such as in furnace systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, choosing the right gasket for your heat exchanger is critical to ensuring long-term performance and efficiency. Whether you’re dealing with high temperatures, fluctuating pressures, or corrosive environments, understanding the types of gaskets and their materials will help you make the best decision for your specific application.
Selecting the wrong gasket can lead to expensive repairs and downtime, so always consider the operating conditions before making your choice.
How to Read P&ID A Complete Guide for Beginners. Click on the below link to Download PDF Now
Read Also
Download Free Piping PDF for Interview Preparation
Download Free Piping PDF for Interview Preparation
What is gasket and their types
What is a valve and its types?
